
Length (feet) = Vd * 1000 feet / (2 * I * Z) Voltage Drop (Vd) = Vd% * Source Voltage / 100 Impedance per 1000 feet (Z) = 1.1 ohms (from NEC Table 9, assuming 10-gauge wire at 0.85 power factor) Now, to calculate the distance, the given parameters are, A table that displays the farthest distances 10 gauge wire can be run at 140☏ and a power factor of 0.9 is given below.
AMPS FOR 10 GAUGE WIRE CODE
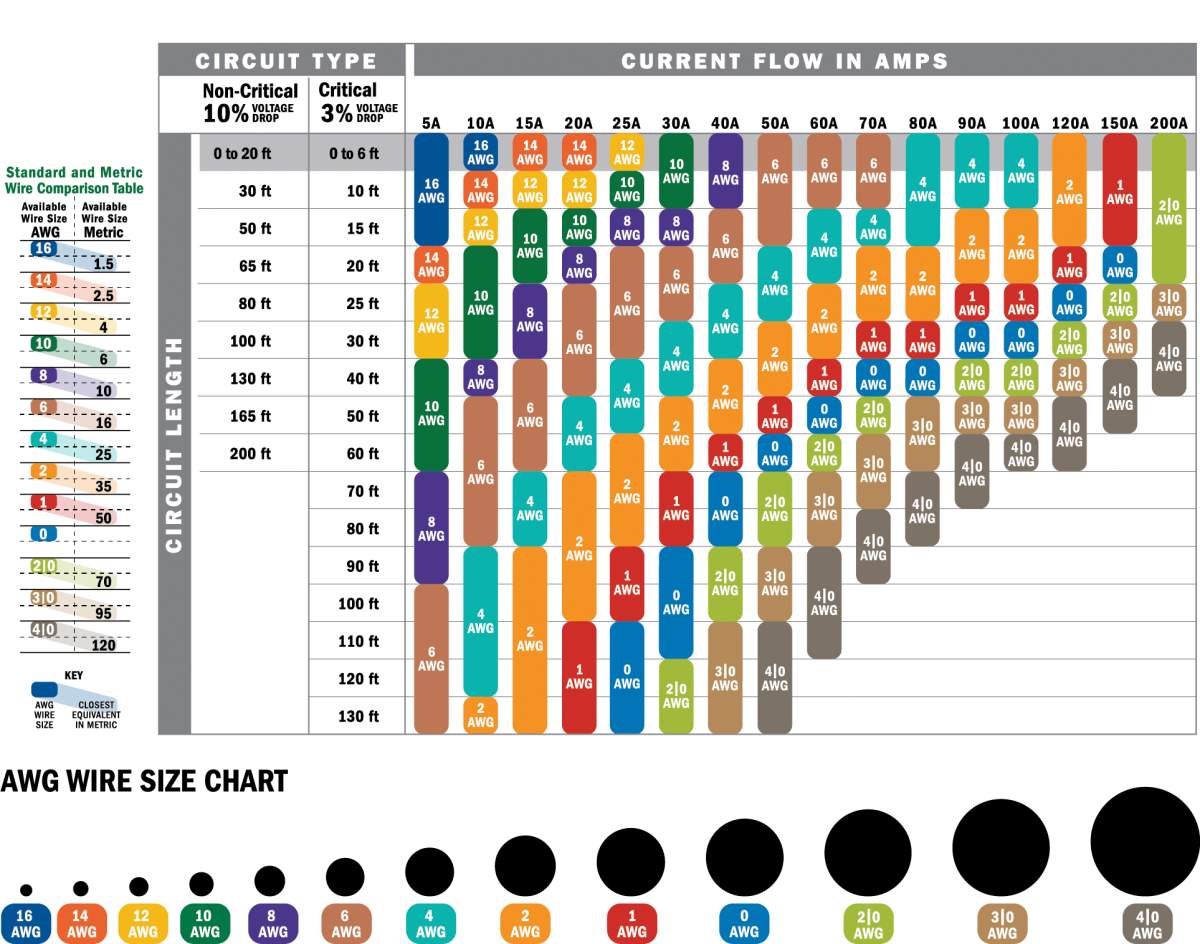
Generally, for branch circuits, the National Electrical Code (NEC) suggests a 3% voltage drop limit. Please note, comments must be approved before they are published.What Is the Approximate Distance a 10 2 Wire Can CoverĬalculate the voltage drop based on the current (amperage) and distance of the wire run to estimate the greatest distance a 10-2 wire can be run safely. Print this out or use the link to this post when you need to reference the chart.ĪSTM International Founded in 1898, ASTM International is a leader in the global standards community. We have provided you with a handy AWG Chart for reference. Both outlet and plug will require a 20 Amp rated wire, so you would need a 12-gauge wire.Īs you can see having a standard like the AWG is important because it determines the amount of electric current (amps) a wire can carry, helping to prevent overheating which will likely cause fire and shock to occur. Your unit will likely have a plug of NEMA 6-20P attached to it. One common residential example of this is the window air conditioning unit. You must factor in the load, number of outlets, and the length of your circuit. Therefore, we suggest you hire an electrician. SAFETY TIP: Electricity is dangerous, if you are even the slightest bit unsure of the project you are working on, hire a certified electrician to complete the project for you. A commonly asked question for DIYs is “How do we determine the proper size and rating for our project?” When installing circuits or working with DIY Wiring Devices, it is important to use wiring that is the right size and rating. One purpose of the circuit breaker and fuse design is to stop the power when overheated, protecting your electrical system and/or device, but you should not let them be your only form of protection. It will be a dangerous situation if you have a device drawing too much power on a circuit with an AWG rating of less than what the device is trying to use. It is important to guard against overheating by using the correct amperage rating. When working on a DIY purchasing the correct gauge wire is more practical. However, using a higher wire gauge than necessary is not economical, because of the higher cost of materials. However, if you try to run 15 Amps of electrical current through a 10-gauge wire, which is typically used for 30 Amps, you will not have any problems. If you try to overload the 14-gauge wire with 30 Amps of current, you will overheat, and the circuit will blow. For example, a 14-gauge wire can safely carry 15 Amps of electrical current. The AWG is the physical size of the wire, but each size wire is only capable of a certain amperage before it becomes dangerously hot and overheats, causing a risk of fire or shock. You can find more information in the ASTM standard B 258.Įach wire gauge has a maximum carrying capacity of electrical current, and amps, it can handle. It is a standard specification for the diameters of round wires used as electrical conductors. The American Wire Gauge (AWG), is a standard wire gauge system that has been used since 1857, mostly in North America.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
